What we do
Ad Scientiam designs, validates and implements digital biomarkers that continuously measure disease progression in real life.
These are derived from data continuously collected via a digital tool, such as the patient's smartphone for example, and transformed by proprietary algorithms.
We concentrate on severe and disabling diseases, particularly in:
- Neuroscience (multiple sclerosis, neuromuscular diseases, etc.)
- Mental disorders (treatment-resistant depression, generalized anxiety disorders, etc.)
- Rare diseases (cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, etc.)


What is a digital biomarker?
Digital biomarkers are physiological and behavioral measures that are clinically-validated and patient-generated collected from digital devices (smartphone first for Ad Scientiam), then processed by algorithms.
1 - Measures
A walking distance, a heartbeat
3 - Digital devices
These assessments are carried out using our applications
2 - Patients
Patients complete independent assessments
4 - Algorithms
Measurements are processed to achieve specific results
These objective, clinically-meaningful data can explain, influence, and/or predict health-related outcomes
The MSCopilot® example
MSCopilot®
The 1st software medical device for multiple sclerosis self-assessment in real-life
Launched in 2018, MSCopilot® is the first and only CE-marked software medical device for the real-life self-assessment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) patients.
Using patients' smartphones, MSCopilot® captures more than 350 digital biomarkers on physiological and behavioral characteristics to objectify MS-related symptoms.
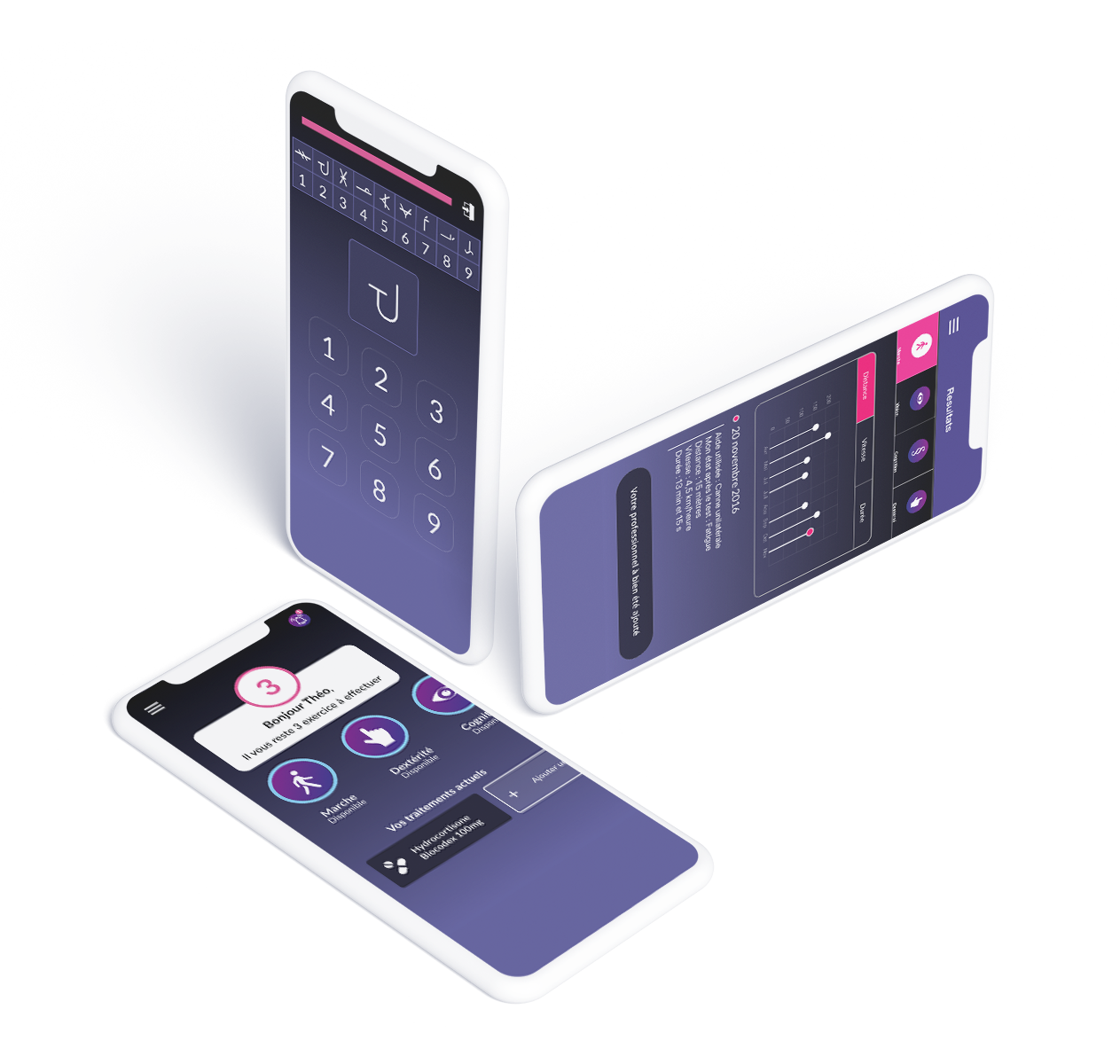



The results generated are shared via a dashboard with the patients' healthcare professionals and provide valuable information to facilitate their clinical decision-making. The patient retains ownership of their data at all times and MSCopilot® is free of charge for patients and healthcare professionals.
MSCopilot®, which currently has over 3,500 users, is also used in several clinical studies.
Discover the 4 MSCopilot® tests! !


Walking assessment
Measure the walking perimeter in real-life conditions The test is to be taken outside, on a flat ground, without obstacle.


Cognition assessment
Measure the attention capacity and the information processing speed. The objective is to decipher a code built with 9 symbols each associated to a number from 1 to 9
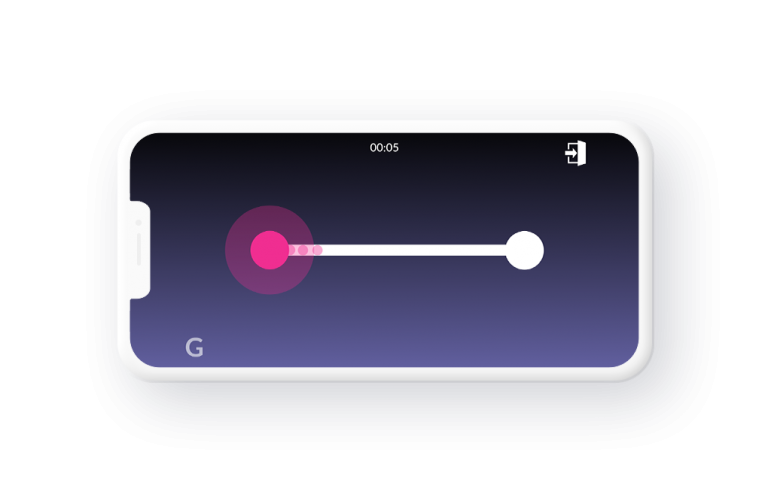

Dexterity assessment
Measure the upper-limb fine motor skills. The goal is to move a sphere with the index finger on a path as accurately and quickly as possible. Both hands will be evaluated..


Vision assessment
Measure the low-contrast visual acuity (at 5%) The goal is to recognize the numbers of decreasing size which appear on the screen of the smartphone.
Pairing with healthcare professionals
Patient-generated assessment results are shared with all healthcare professionals who follow the patient.
The latter remains in control of their data and can withdraw access to his evaluation results at any time.
Results monitoring
To easily follow the evolution of their patients, the healthcare professional has a dashboard, a secure space dedicated to them to view the results of their patients.
They will also be able to read, analyze and interpret the results directly on the patient's phone on the day of the consultation.

